Effective Communication
Elements of Communication
- Source: sender, teacher, speaker
- Symbols: words, signs, props
- Receiver: listener, student
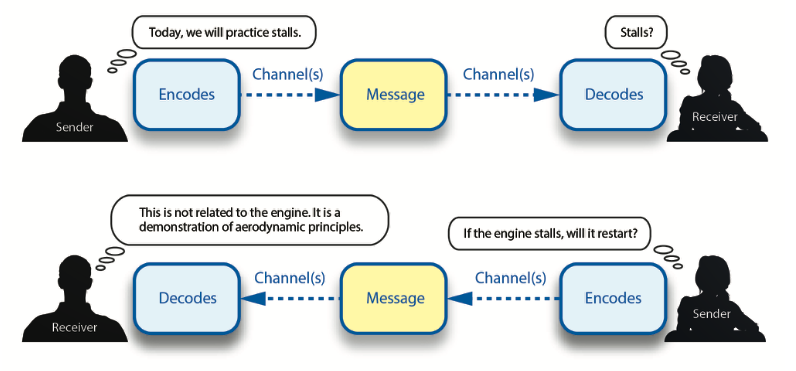
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 4-2
Barriers to Communication
- Lack of common experience
- Communication can only be effective when there are experiences that are similar to what is being described
- The learner's experience determines how they interpret symbols
- For example, using aviation terminology before the learner has learned the vocabulary
- Confusion between the symbol and the object
- Misunderstanding between a symbol that the listener interprets and the one intended by the speaker
- Overuse of abstractions
- Using words are concepts that are too general
- For example, "aircraft" could be a helicopter, airplane, airship
- Interference
- Somehow the message is cut short or disrupted, but the listener isn't aware
- External factors
- Difficulty hearing, external pressures, external pressures, multitasking
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 4-4
Developing Communication Skills
- Role playing
- Practice instruction communication with someone other than a student
- Listening
- Do not interrupt
- Do not judge
- Think before answering
- Be close enough to hear
- Watch nonverbal cues
- Beware of biases
- Look for underlying feeling
- Concentrate
- Don't rehearse answers while listening
- Do not insist on the last word
- Questioning
- Open-ended questions are good for large concepts
- Closed-ended questions are good when you want a specific answer
- Paraphrasing an answer back to the learner can be helpful
- Instruction enhancement
- Always keep learning as an instructor