Assessment
The purpose of an assessment is to check how learning is progressing, and will provide practical feedback for both the learning and instructor.
Characteristics of Effective Assessment
- Objective: Bias should not be present, test should be honest
- Flexible: Tone of the assessment should fit the occasion
- Acceptable: The learner must accept why they are being assessed
- Comprehensive: Should cover all areas needed
- Constructive: Praise where appropriate
- Thoughtful: Respect the learners feelings
- Specific: Give specific, actionable feedback
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-2
Traditional Assessments
Traditional tests are generally written tests with questions like multiple choice, true-false, fill in the blank, and have a time limit.
Good written tests should exhibit:
- Reliability: Consistent when repeated with different students and graders
- Validity: Measuring what it's intended to measure
- Usability: Easy to read and complete
- Objectivity: Single scoring of a given test
- Comprehensiveness: Cover the range of learning required
- Discrimination: How well it measures the quality of the performance
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-3
Authentic Assessment
A comprehensive assessment involves students to perform real-world tasks and demonstrate application of skill.
Learner-Centered Assessment
A four-step series of open-ended questions which guides the learner through a self-assessment:
- Replay: Have the learner recount a flight or procedure, interject when the account does not seem accurate. This lets the learner evaluate their own perceptions
- Reconstruct: Ask the learner to identify could have done differently
- Reflect: Imbue experiences with meaning by having the learner reflect on the experience
- Redirect: Have the student consider how they might apply these learnings in future scenarios
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-5
Maneuver or Procedure "Grades"
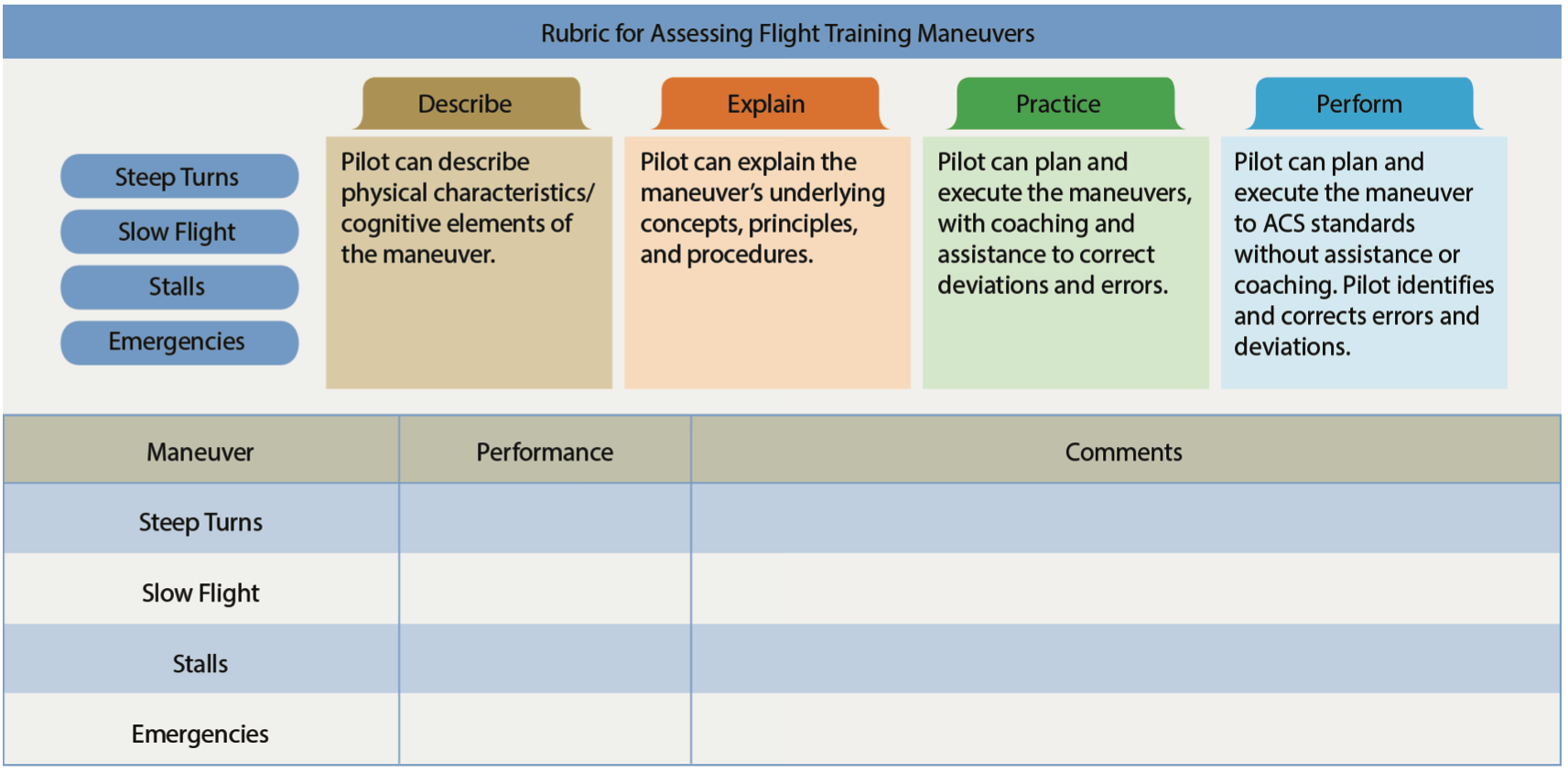
- Describe: Learner can describe elements of the maneuver, but need assistance to do it
- Explain: Learner understands the concepts and procedure, but needs assistance to do it
- Practice: Learner can plan an execute the scenario, but some coaching/correct is required
- Perform: Learner can perform activity without instructor assistance
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-6
Assessing Risk Management Skills
- Explain: Learning can identify, describe, and understand risks, but needs prompting to make decisions
- Practice: Learner can apply SRM principles to real situation, with some corrections or coaching. Learner is active decision maker
- Manage/Decision: Learner can gather and evaluate information and make an autonomous decision
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-6
Choosing an Effective Assessment
- Determine level-of-learning: Pick one of the level of learning
- List indicators of desired behaviors: Determine what would indicate achievement of assessment objective
- Establish criterion objectives: Define performance-based objectives and targets
- Develop criterion-referenced test items: Develop questions or activities which target the specific criterion objectives
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-8
Critiques and Oral Assessments
Critiques are instructor-learner assessments.
There are several types that can be used:
- Instructor/learner: Learners are offered to criticize a performance
- Learner-led: Learners lead the critique
- Small group: Learners are divided and critique in groups
- Self-critique: A learner critiques their own performance
- Written: Critique in writing, which may be more thoughtful or thorough
Oral Assessments
Oral assessment are direct questioning of a learner by an instructor.
Aviation Instructor's Handbook pg. 6-11
Characteristics of Effective Questions
- Questions should be written in advance
- Questions can be fact questions (rote) or thinking questions (HOTS)
Questions should be:
- About the subject at hand
- Brief and concise, clear and definite
- Adapted to the experience level of the learner
- Center on one idea
- Persist a challenge to the learner
Types of Questions to Avoid
- Bewildering questions
- Oversize questions
- Toss-up
- Trick questions
- Irrelevant questions
Answering Learner Questions
- Think before you answer
- Don't introduce more complex topics in your answer if its not necessary
- After responding, gauge how the student reacted to your answer