Teaching Airspace
This is a basic lesson breakdown of the different components of airspace, spread over multiple lessons.
5 Cases of Airspaces
- 1 mile, clear of clouds
- 3 mile, clear of clouds
- 1 miles, 500' below, 1000' above, 2000' horizontally
- 1 miles, 500' below, 1000' above, 2000' horizontally
- 5 miles, 1000' below, 1000' above, 1.sm horizontally
Lesson 1: Identifying Airspace
- Find airspace on the legend, then identify that airspace somewhere on the chart
- Class B: Blue solid line
- Class C: Magenta solid line
- Class D: Blue dashed line
- Class E at surface: Magenta dashed line
- Used for non-precision approaches around non-towered airports
- Class E at 700': Purple shading
- Class E at 1200' AGL: Blue shading
- These are exceptions to Class E starting at 1200' AGL
- Within these cutouts, Class G goes from the surface up to 14,500'
- These airspaces are going away, and most of them have been decommissioned
- ATC cannot clear you GPS direct through this big block of Class G
- Class E "zipper lines"
- Shows a boundary where Class E abuts Class G below it
Lesson 2: Cloud Clearance and Visibilities
- 1 mile, clear of clouds
- Class G airspace, up to but no including 1200 AGL
- 3 mile, clear of clouds
- Class B Airspace
- 1 miles, 500' below, 1000' above, 2000' horizontally
- Class G above 1200 AGL, < 10,000' MSL
- 3 miles, 500' below, 1000' above, 2000' horizontally
- Class C, D, and E below 10,000' MSL
- Class G < 10,000' MSL at night
- 5 miles, 1000' below, 1000' above, 1 s.m horizontally
- Class E or G above 10,000' MSL
In Class G airspace, you may operate under VFR with in 1/2 mile of an airport runway:
- during the day as long as the visibility is at least 1 statute mile and you remain clear of clouds
- at night, as long as the visibility is at least 3 statute miles and you remain clear of clouds
Lesson 3: Speed Limits and Entry Requirements
- Speed limits
- < 10,000' MSL: 250 knots
- In Class B Airspace: 250 knots
- Below Class B or in a Class B corridor: 200 knots
- Class D and C airspace within 4nm up to 2500 AGL: 200 knots
- Certificate requirements
- Class G requires a pilot certificate
- Class E below 10,000': A pilot certificate, no transponder
- Class E above 10,000': A pilot certificate and a transponder
- Class D: Establish 2-way communications (exchange of call sign and facility name)
- Class C: Establish 2-way communications (exchange of call sign and facility name), inside and above requires a transponder
- Class B:
- 2-way communication with a specific clearance into the airspace
- Student pilot certificate minimum
- Some airports require a minimum of a private pilot certificate in Part 91 Appendix D
- Class A:
- On an instrument flight plan
- Automatic Dependent Surveillance: Broadcast (ADS-B)
- Required everywhere a transponder is required
- Plus one additional place: Within 12nm of the shoreline of the Gulf of Mexico between 3000 MSL and 10,000 MSL
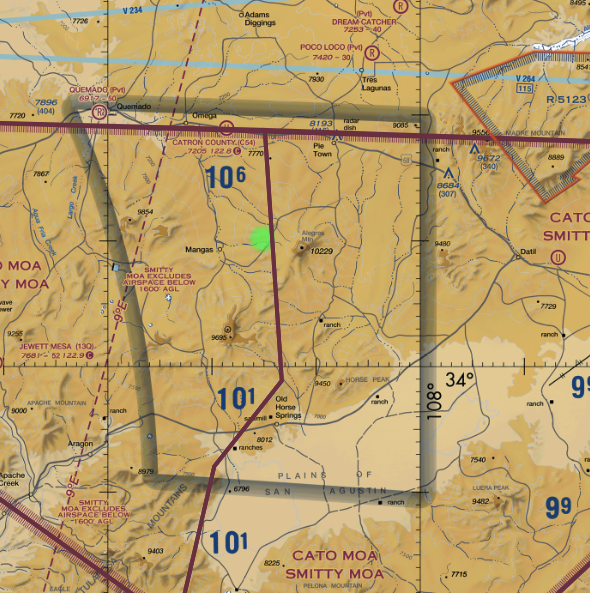
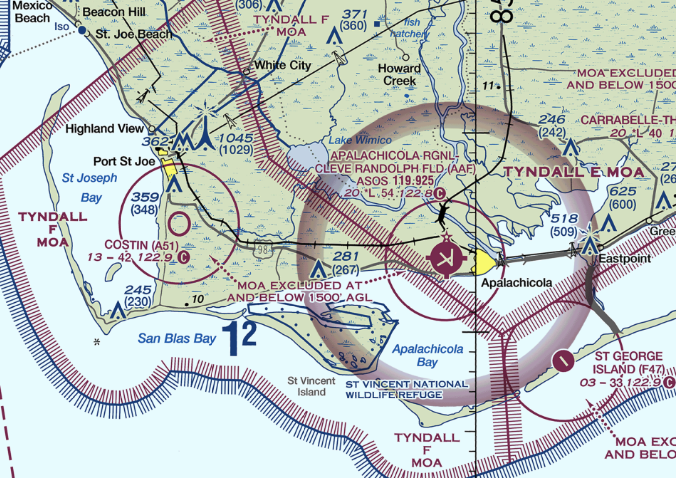
Lesson 4: Special Use Airspace and SVFR
Special Use Airspace
- Terminal Radar Service Area (TRSA)
- Class C-level radar service within the TRSA
- Participation is not mandatory
- MOA
- No clearance required
- Find active times on the sectional legend
- Alert area
- No clearance required
- Concentrated flight training
- Participation is voluntary
- Restricted Areas
- Needs a clearance to enter ("cleared into" the airspace)
- Prohibited area
- Cannot be entered
- Warning areas
- Do not required a clearance, but is not recommended
- MOA exclusion area
- Indicates an area around an airport which is excluded from a MOA
- Military training routes (MTR)
- IR: Instrument routes
- VR: Visual routes
- 4 digits: < 1500'
- 3 digits: > 1500'
- Special Flight Rules Area (SFRA)
- Washington SFRA requires an online course and a clearance
- The Grand Canyon also has an SFRA
- Temporary Flight Restrictions (TFRs)
Special VFR
- The pilot must ask the controller
- Maintain 1 mile visibility and clear of clouds
- At night, pilot must be instrument rating and the aircraft instrument equipped
- Some Class B airspace will prohibit SVFR with "NO SVFR"